Please read the rules about how the modeler works.
It describes the meaning and behavior of each shape.
Scroll down the page to read the directions for how to use the interface.

The value of a shape is determined by its color according to this spectrum.
Click on the 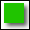 , ,  , ,  , or , or  buttons to create a new shape. Drag a shape to move it. Click a shape to select it, then drag a black tab in one of the corners or sides to resize the shape. Press '1' on the keyboard to set the value of a selected shape to 10 (dark gray), '2' to set the selected shape's value to 20 (light gray), and so on. '0' sets the selected shape's value to 100 (red). Press the '+' key on the keyboard to increment tthe selected shape's value by 1. Press the '-' key on the keyboard to decrement tthe selected shape's value by 1. buttons to create a new shape. Drag a shape to move it. Click a shape to select it, then drag a black tab in one of the corners or sides to resize the shape. Press '1' on the keyboard to set the value of a selected shape to 10 (dark gray), '2' to set the selected shape's value to 20 (light gray), and so on. '0' sets the selected shape's value to 100 (red). Press the '+' key on the keyboard to increment tthe selected shape's value by 1. Press the '-' key on the keyboard to decrement tthe selected shape's value by 1.
 are levels in system dynamics models. Think of them as containers of water. Place one square on top of another to connect them, allowing "water" to flow from the top tank to the bottom tank. are levels in system dynamics models. Think of them as containers of water. Place one square on top of another to connect them, allowing "water" to flow from the top tank to the bottom tank.
 and and  are rates in system dynamics models. Think of them as valves that control the flow of water between two containers. are rates in system dynamics models. Think of them as valves that control the flow of water between two containers.
 allow water to flow faster when there is more water in the source container. allow water to flow faster when there is more water in the source container.
 allow water to flow faster when there is less water in the source container. allow water to flow faster when there is less water in the source container.
 are used to facilitate feed back loops. They bring water from the bottom levels back up to a higher level. They always come in pairs. are used to facilitate feed back loops. They bring water from the bottom levels back up to a higher level. They always come in pairs.
 deletes a selected shape. deletes a selected shape.
 moves a selected shape up one level. moves a selected shape up one level.
 moves a selected shape down one level. moves a selected shape down one level.
 moves a selected shape up to the top level. moves a selected shape up to the top level.
 moves a selected shape down to the bottom level. moves a selected shape down to the bottom level.
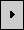 starts the simulation of the model you have built. If you have levels that are connected (i.e. you have overlapping squares), the color of the levels will start to change to show the changing water levels. If no levels are connected or all the water has reached the lowest level that it can in the current model, no color change will take place. starts the simulation of the model you have built. If you have levels that are connected (i.e. you have overlapping squares), the color of the levels will start to change to show the changing water levels. If no levels are connected or all the water has reached the lowest level that it can in the current model, no color change will take place.
 steps through one cycle of the simulation. steps through one cycle of the simulation.
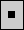 stops the simulation. stops the simulation.
 changes the speed of the simulation. 0 is the slowest. 10 is the fastest. "Sim Speed" controls how often the model is updated. "Step Size" controls how big of a change is made on every update. A high "Sim Speed" and a low "Step Size" will create a smooth, gradual color change. A low "Sim Speed" and a high "Step Size" will create infrequent but large changes in color. changes the speed of the simulation. 0 is the slowest. 10 is the fastest. "Sim Speed" controls how often the model is updated. "Step Size" controls how big of a change is made on every update. A high "Sim Speed" and a low "Step Size" will create a smooth, gradual color change. A low "Sim Speed" and a high "Step Size" will create infrequent but large changes in color.
Demo versions and earlier notes on the Constructivist Modeler are still available.
created by Josh Weihnacht
last updated 3/30/00
|